Divergent boundaries -- where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from. There are four types of plate boundaries.

Understanding The Fundamentals Of Earthquake Signal Sensing Networks Analog Devices
5657 Other modes of wave propagation exist than those described in this article.

. Different types of legacy data and newly acquired geo- and petrophysical as well as geochemical-mineralogical measurements form the basis of an integrated geological interpretation of the. Wave earthquake sonic boom explosion sound through air or the natural frequency of a body in motion. In some specific areas a structural engineer may be required to.
Even light part particle part wave has a fundamen-tal frequency which can be observed as color. List of Notable and Major California Earthquakes Californias Earthquake History. Knowledge of earthquake processes and earth structure comes from both forward modeling and inversion of earthquake travel-time and ground-shaking data.
Most movement occurs along narrow zones between plates where the results of plate-tectonic forces are most evident. Among the many types of seismic waves one can make a broad distinction between body waves which travel through the Earth and surface waves which travel at the Earths surface. Sensors can convert these forces into electrical signals that you can observe and study with an.
Magnitude is expressed in whole numbers and decimal fractions. Shaking at a given site say one of engineering interest is controlled by. For example a magnitude 53 is a moderate earthquake and a 63 is a strong earthquake.
In most cases the foundation plan will include footing sizes and locations footing details and other important information needed to properly construct the home. Because of the logarithmic basis of the scale each whole number increase in magnitude represents a tenfold. Though of comparatively minor importance for earth-borne waves they are important in the case of.
The Modified Mercalli intensity scale MM MMI or MCS developed from Giuseppe Mercallis Mercalli intensity scale of 1902 is a seismic intensity scale used for measuring the intensity of shaking produced by an earthquakeIt measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location distinguished from the earthquakes inherent force or strength as measured by seismic. Foundation plans describe to the builder the type of foundation requested by the home owner or the type of foundation required by a certain geographic area. The amount pattern direction and timing of slip on the fault The distance of the site from the fault The types of geologic structures and materials along the.
Scientists now have a fairly good understanding of how the plates move and how such movements relate to earthquake activity. Although earlier earthquakes have been documentedsuch as significant movement on the southern San Andreas fault all the way back to the 1600sthe earliest reported earthquake in California was on July 28 1769 noted by members of a Spanish expedition to chart a land route from San Diego to. Energy vibrating particles and other invisible forces pervade our physical uni-verse.
See the Intensity section below for more details on shaking intensity measurements.

Earthquakes General Interest Publication

How Are Earthquakes Measured Magnitude Intensity Scales Cea

Earthquake Graphic Organizers Covers Types Of Faults Earthquake Waves Measuring Earthquak Graphic Organizers Earth Science Lesson Plans Earth Science Lessons

Earthquakes And Interior Of The Earth Seismic Seismic Wave Earth Lessons
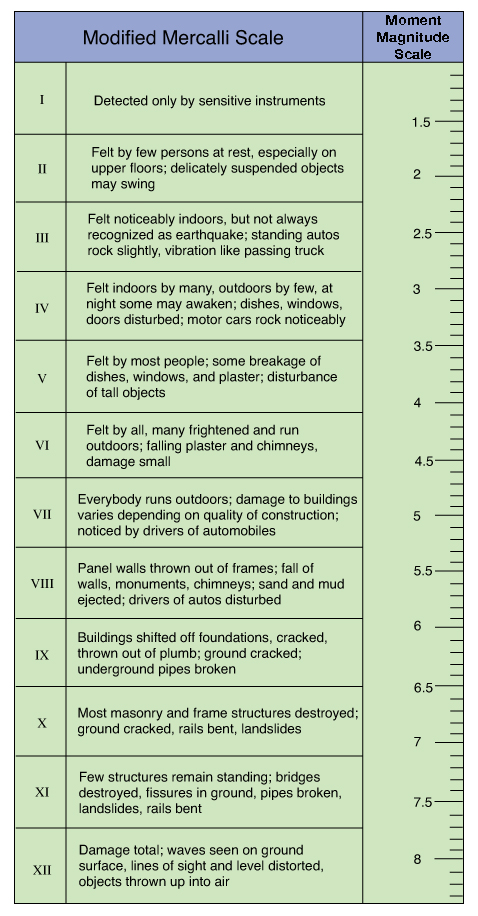
Measuring Earthquake Magnitude And Intensity Geokansas

A Tsunami Warning System Tws Is Used To Detect Tsunamis In Advance And Issue Warnings To Prevent Loss Of Life And Damage It Is Tsunami Warning Tsunami System

0 Comments